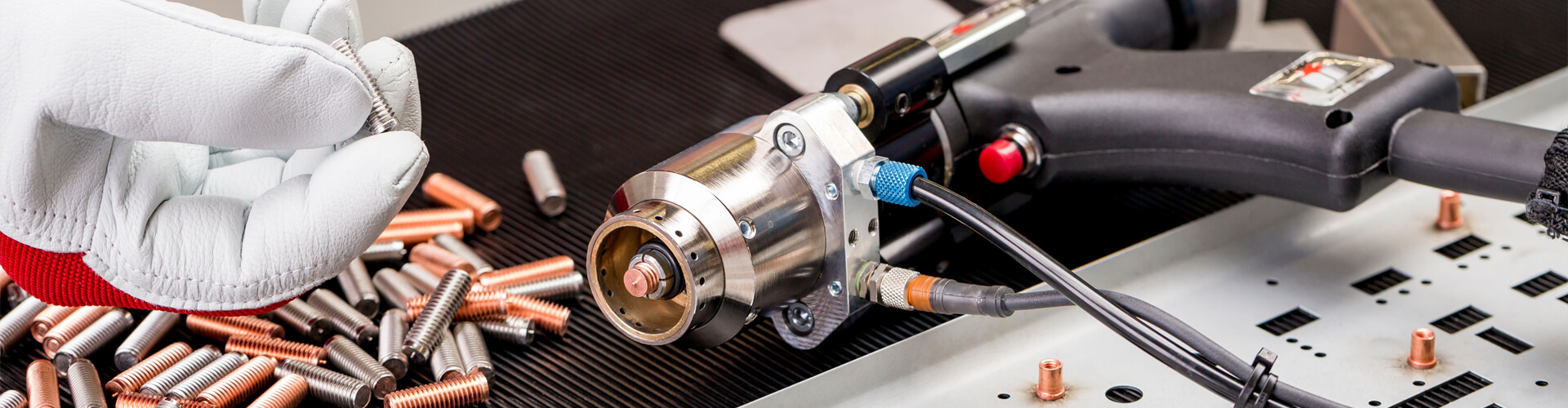
Stud welding
Everything you ever wanted to know about stud welding
On the following pages you will find the basics, functionality, areas of application and all other information relevant to stud welding.
What is stud welding?
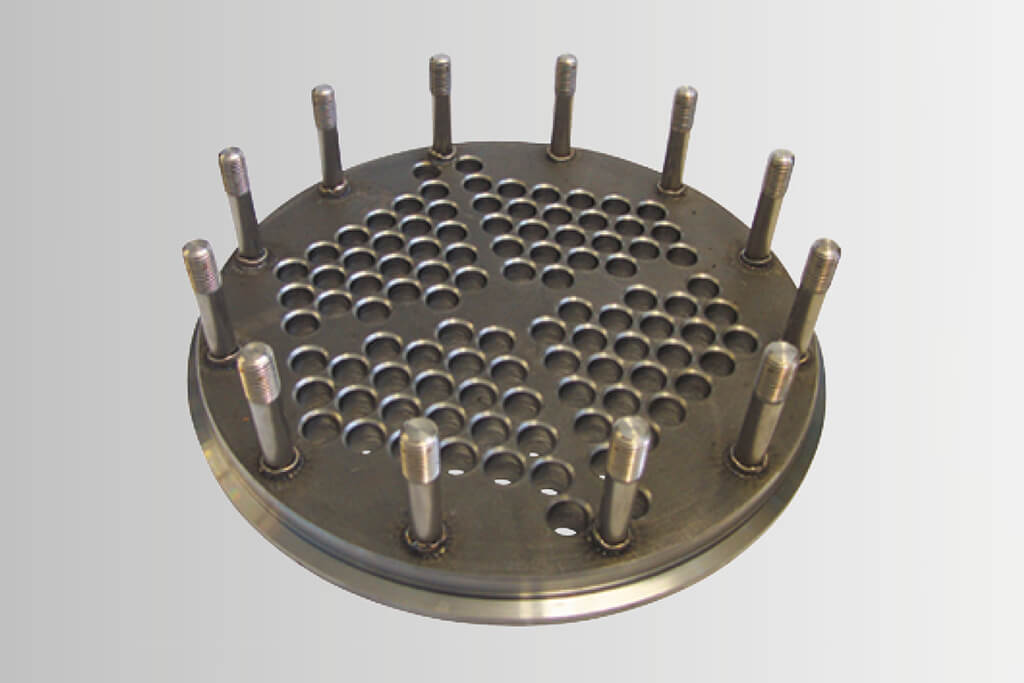
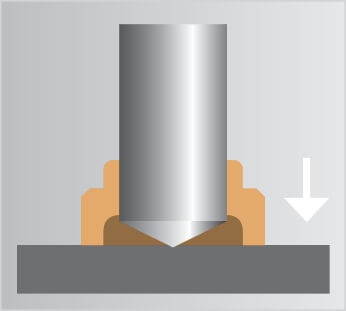
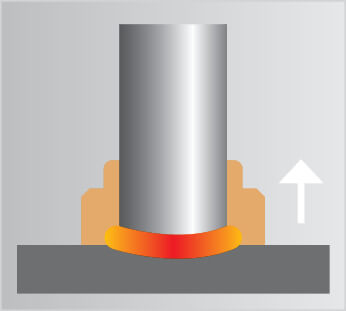
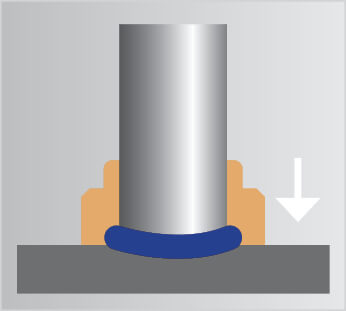
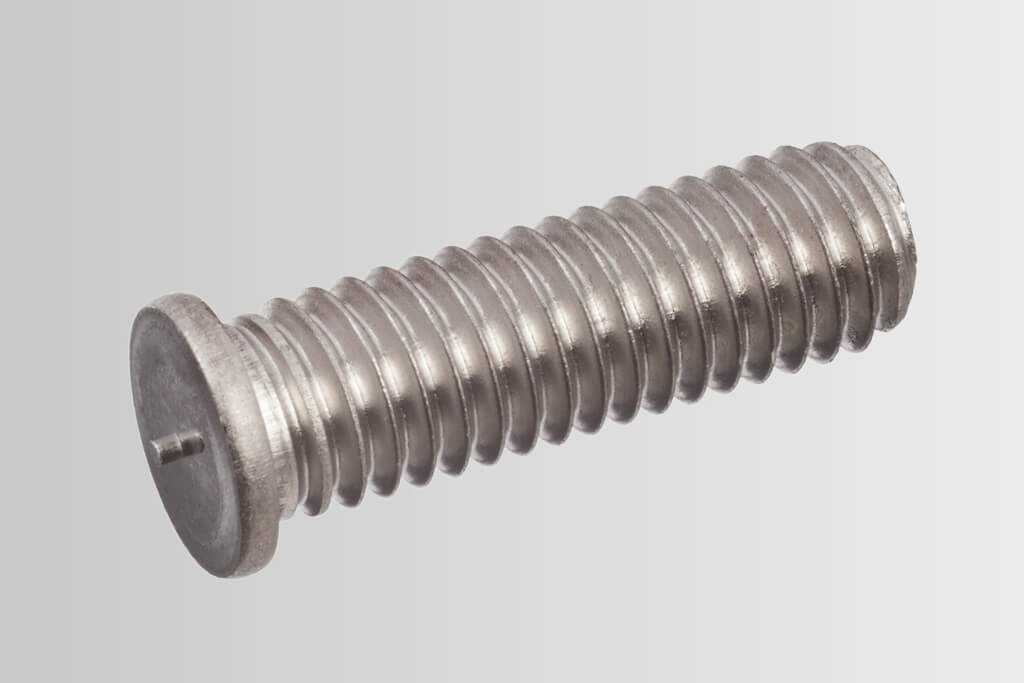
Stud welding allows metal fasteners such as weld studs, weld pins and tapped studs, to be welded onto another metal object using an electric arc at lightning speed. An electric arc is created between the end of the stud and the surface of the workpiece, melting both parts. The stud is then forged into the molten pool. The material solidifies and the stud is welded. The weld is uniform and has complete fusion across the flange. As the whole surface of the weld stud is joined to the workpiece, the resulting weld joint is stronger than the stud or parent material.
Since no holes are punched in the sheet, the workpiece is not weakened and corrosion problems are minimized. When welding the stud, access is only required from one side making handling the component much easier especially when establishing an earth connection.
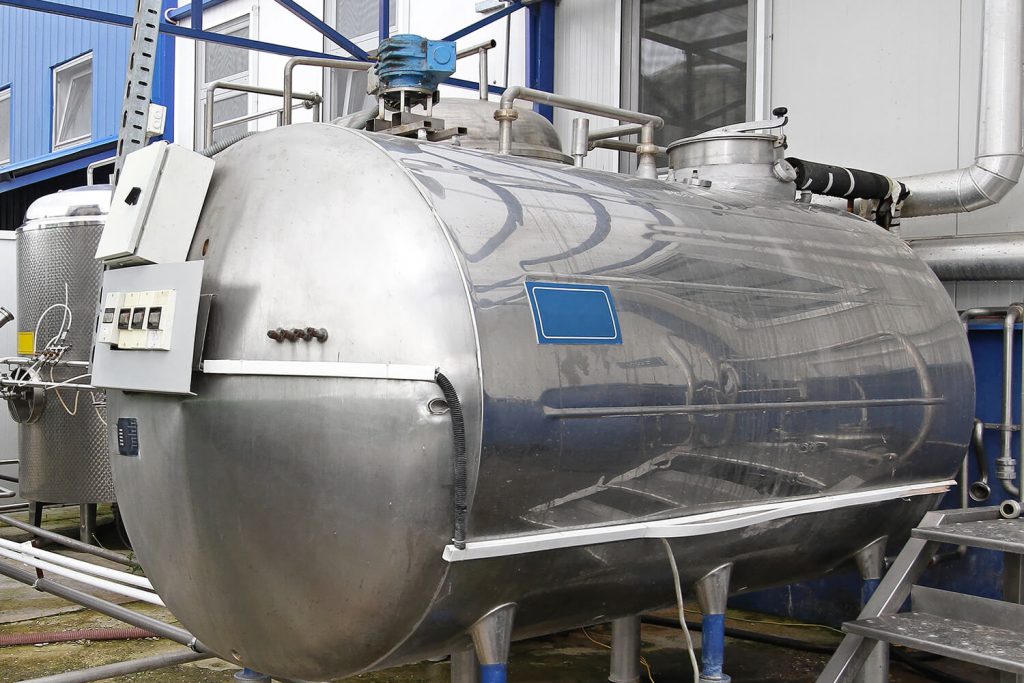
This absolutely leakproof, hole-free and decorative joining technique is used in many everyday objects and facilitates their handling. Be it coffee machines, cooking pots, flat irons, steam cookers or even in vehicles and roofing – many things would be impossible without stud welding.
With the development of the patented “SRM Technology®” procedure (patent no. 10 2004 051 389) it has even been possible to replace many areas of gluing, riveting, punching and drilling.





The advantages of stud welding:
- Wide range of use from Ø 2 mm up to Ø 25 mm
- Complete fusion, hence high strength
- Weldable even on thin sheet metal
- No or only very little reverse marking
- No changes in material such as deformation or distortion
- No drill holes required, hence no leaking
- Corrosion problems can be minimized
- Access to parts only required from one side
- Various material combinations possible
- No time and cost consuming preparatory and finishing works necessary
- Fast and easy operation ensure high productivity
- Can be easily automated with standard weld studs
Capacitor Discharge
Capacitor discharge welding in detail
Capacitor discharge stud welding has been successfully used for many years all over the world. It allows weld studs with a maximum diameter of M12 to be welded. The welding process is executed by discharging the capacitor battery within a fraction of a second from 1 – 3 ms (0.001 – 0.003 sec.) using the welding element’s ignition tip.
This procedure has proven invaluable especially in vehicle construction, sheet metal forming and decorative metal design.
Picture gallery of CD welding
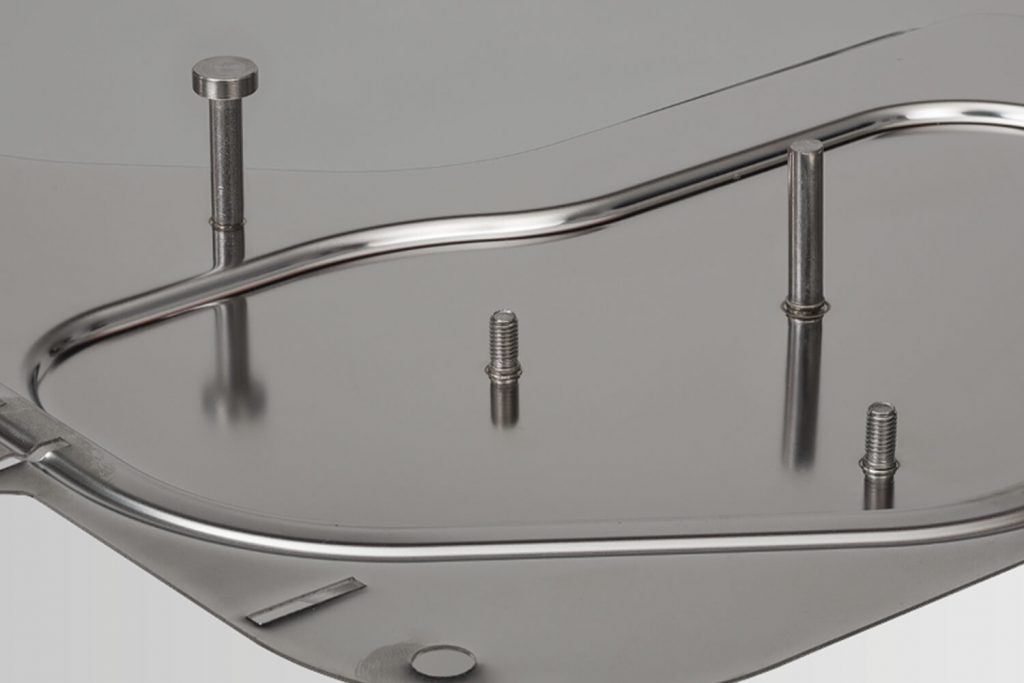

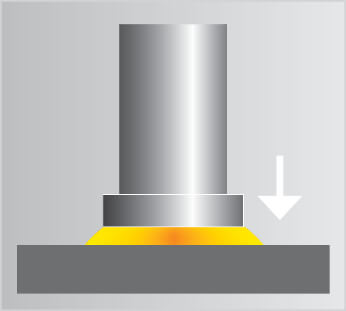
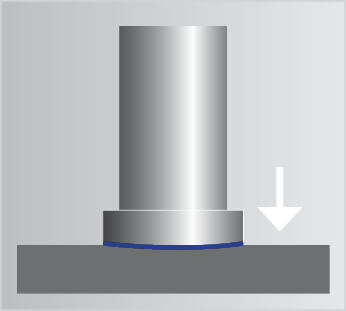



Video on CD stud welding
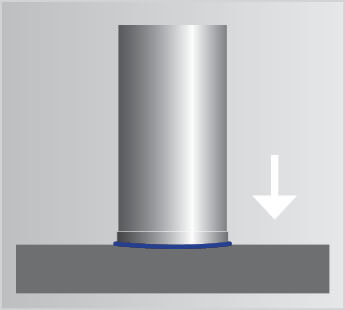
SRM Technology®
Made by Soyer

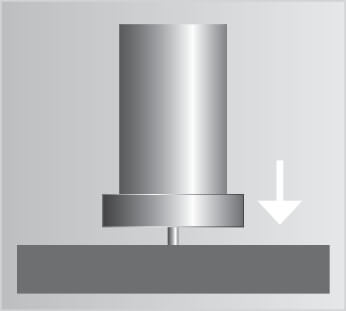
The patented stud welding process in the radial symmetrical magnetic field (patent no.: 10 2004 051 389) in conjunction with the innovative HZ-1 universal weld stud featuring a plane end face and centering tip enables the safe and clean welding of weld studs up to M16. In this process, the use of ceramic rings is no longer needed. This procedure opens up whole new possibilities especially in automated stud welding plants and large-scale component production.
Picture gallery of SRM stud welding

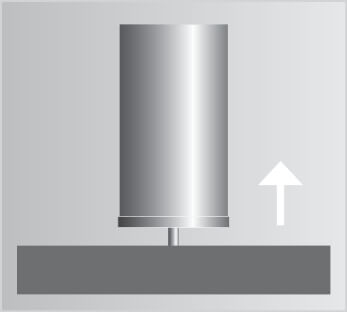
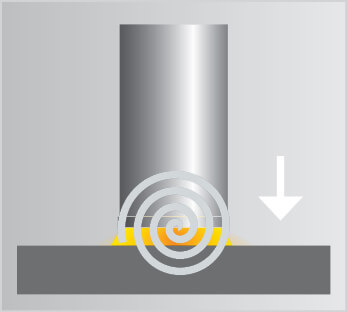


Videos on SRM stud welding
Drawn Arc
With ceramic ring or protective gas in detail
Drawn arc stud welding is a welding procedure for maximum loads. It enables welding of weld fasteners measuring between 6 mm and 25 mm in diameter. The entire welding process is controlled and monitored by an electronic power source.
This procedure creates high-quality welded connections and has proven invaluable in steel construction, mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, construction of prefabricated parts made from reinforced concrete, door and window construction, structural and civil engineering, fixture and pipeline construction.